Weight Loss Statistics By Country, Demographic and Type

Page Contents
- Introduction
- Editor’s Choice
- General Weight Loss Statistics
- How Does Weight Gain Affect People- Facts
- Weight Loss Statistics By Type
- Weight Loss Statistics By Country
- Weight Loss Statistics By Demographic
- Weight Loss Success Statistics
- Impact on Health
- Impact on Economy
- Reason Behind Weight Loss Statistics
- Covid-19 and Weight Loss Statistics
- Trends and Predictions
- Final Thoughts
Introduction
Weight Loss Statistics: As more individuals strive to lead healthier lifestyles and combat the obesity pandemic, weight reduction has become an integral component of modern culture. Statistics regarding this subject provide invaluable insight into its frequency, difficulty, and results. Recent statistics demonstrate the need for effective weight control techniques: 13% of individuals globally are classified as obese while 39% are overweight. These figures underscore the necessity of effective methods of managing one's weight. Studies show that an estimated 45 million people in the US make efforts each year to lose weight; however, not everyone succeeds and only a small fraction manage to maintain their ideal weight over the long term.
According to research, only 20% of those who first lose weight manage to keep it off permanently. Despite these challenges, many still prioritize weight loss, using strategies such as diet changes, exercise routines, and lifestyle modifications in their quest to shed extra pounds. Strategies for combatting this global health concern should reflect an extensive knowledge of data associated with weight loss.
Editor’s Choice
- 44 percent of North Americans have successfully shed excess weight
- East Asia and the Pacific account for 33.1% of the population who have lost weight
- 5% of populations in Central Asia and Europe have successfully shed extra weight
- 8% of people living in the Middle East and North Africa have successfully shed excess weight
- 9 of the participants used exercise successfully; to reduce weight
- 62% reduced food consumption; while 50% increased their fruit and vegetable intake
- 7% of individuals attempt to shed unwanted weight by drinking more water
- 7 percent have made efforts; to consume less unhealthy food
- 7% of respondents indicated; the need to alter their eating habits in some way
- Adults who engage in regular physical exercise; take their medicine 46% of the time
- Other studies estimate that; only 19.3% of Americans engage in physical exercise or sport on an everyday basis
- Men participate in physical activity more regularly than women (20.7% vs 18%)
General Weight Loss Statistics
People often look to weight loss as an avenue for improving their health, physical appearance, and overall well-being.
- Over time, obesity rates worldwide have seen a steady rise. According to World Health Organization statistics from 2022, over 1.9 billion persons were overweight while 655 million individuals were considered obese – that means 13% are classified as obese while 39% fall within overweight categories.
- Weight loss is an obvious goal. A recent estimate indicates that over 45 million individuals make efforts annually in the US alone to shed their excess weight, showing both social and personal commitment to solving weight-related issues.
- Long-term weight loss may be difficult. According to studies, only a minority of those who begin weight reduction programs ultimately manage to keep their target weight for an extended period. According to one research paper, only 20% of people who initially lose weight successfully maintain it over time; though these figures could vary depending on factors like the technique used, personal dedication levels, and support networks already in place.
- 5% of those classified as overweight or at a healthy weight attempted to weight loss at some point.
- Obesity is more prevalent among certain ethnic/racial minorities, those living on lower incomes and with less education.
- Yo-yo dieting (sometimes referred to as weight cycling) refers to a condition in which people often lose and gain weight rapidly, with nearly 80% eventually regaining it, sometimes even increasing weight overall! As such, lifestyle modifications rather than quick solutions must be adopted for weight reduction to take hold.
- Losing weight can have numerous health advantages. Studies have linked it with reduced risks of chronic conditions like type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, malignancies, and musculoskeletal issues; plus blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and general quality of life improvements from losing extra weight.
- 9 of the participants used exercise successfully; to reduce weight
- 62% reduced food consumption; while 50% increased their fruit and vegetable intake
- 7% of individuals attempt to shed unwanted weight by drinking more water
- 7 percent have made efforts; to consume less unhealthy food
- 7% of respondents indicated; the need to alter their eating habits in some way
- Adults who engage in regular physical exercise; take their medicine 46% of the time
- Other studies estimate that; only 19.3% of Americans engage in physical exercise or sport on an everyday basis.
- There are various techniques for losing weight, from diet adjustments and exercise routines to medicinal therapies and surgical operations. Calorie restriction, low-carb diets, intermittent fasting, and increasing physical activity are some common weight-loss strategies; each approach may vary in terms of efficacy – therefore it's essential that you select one which meets both your preferences and health requirements.
- Studies show that having accountability and support systems in place can aid individuals in losing weight more successfully. This could involve consulting healthcare specialists, joining support groups or behavior modification programs as well as using wearable technology or smartphone applications that track progress while offering encouragement.
- Weight loss struggles can have profoundly detrimental psychological consequences. People may experience changes to self-esteem, body image issues, and emotional struggles during this process, making it crucial to address all psychological factors as part of an integrated plan for wellness.
How Does Weight Gain Affect People- Facts
Weight gain can have far-reaching negative impacts on one's physical and mental health.
- Gaining weight has been linked with an increased risk of various conditions, including type 2 diabetes; cardiovascular disease, various malignancies, and musculoskeletal issues.
- According to the World Health Organization (WHO), obesity causes approximately 2.8 million deaths annually worldwide and poses an increased risk for noncommunicable illnesses.
- Weight gain may have negative psychological repercussions for those affected, including low self-esteem and body dissatisfaction, as well as an increased chance of depression or anxiety.
- Research indicates that stigma and prejudice related to one's weight could make those who have gained weight even worse about themselves.
- Studies indicate that weight gain may significantly impact a person's general health and quality of life, with limitations in daily activities, reduced physical function, decreased energy levels, and limited mobility being key outcomes of weight gain.
- Weight issues can have a detrimental impact on relationships and social interactions, research indicates. People who have put on weight may encounter social exclusion, prejudice, and stigma due to their condition resulting in feelings of shame and decreased support from loved ones.
- Becoming obese and overweight can cost individuals and society an exorbitant sum in financial losses. Obesity costs both patients and society money in healthcare expenditures, productivity losses, and reduced quality of life issues that adversely impact both them and healthcare systems.
- Over time, gradual weight gain can drastically reduce life expectancy and increase the risk of chronic diseases.
- Studies published in The New England Journal of Medicine demonstrated that individuals who were overweight or obese during their middle years were at greater risk of shortening their lives and experiencing chronic illnesses than those without these characteristics.
Weight Loss Statistics By Type
There are various strategies available for weight loss, from making changes to your diet and exercising regularly, to medical treatments or surgical operations.
- Low-calorie diets are an increasingly popular method for weight loss, according to studies. A typical low-calorie diet typically comprises between 800 and 1500 calories daily.
- Low-carb diets restrict carbohydrates while increasing protein and fat consumption, according to research. Studies show that following such a plan can help people shed weight more rapidly than when following low-fat diets.
- Diets with Mediterranean influences have long been linked with weight loss and improved cardiovascular health, due to the abundance of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean meats, and healthy fats within them.
- There are currently 64 million gym members in the US.
- 49 million Americans regularly run or jog; yet that number continues to decrease.
- 94% of people who lose weight improve their physical activity levels by increasing walking.
- Nearly 40% of individuals report that dieting is undertaken to help them achieve weight loss.
- About 30% wanted to avoid weight gain.
- Every year; supplements for weight loss generate sales worth $2.1 billion alone.
- 28% of individuals believe that every calorie has the same impact on weight growth.
- Regular aerobic exercises like cycling, swimming, or jogging can help you to shed extra weight. According to studies, combining aerobic activity with diet changes yields greater results in terms of weight reduction than just dieting alone.
- Resistance training such as bodyweight exercises and weightlifting can help to build muscle while decreasing fat. Weight reduction and improved body composition could result from this practice.
- Research suggests HIIT is an effective strategy for weight loss and cardiovascular fitness improvement. By engaging in quick bursts of intense training separated by rest intervals, HIIT can provide effective weight-loss and cardiovascular fitness improvement techniques.
- Prescription weight-loss drugs can provide significant assistance with weight loss when taken as prescribed by a physician. They usually increase metabolism, decrease nutrition absorption or curb appetite to aid weight reduction.
- Seriously obese individuals may be candidates for bariatric surgery. Procedures like gastric bypass, gastric sleeve, and adjustable gastric banding are being offered as solutions to achieve significant weight loss with improved health outcomes.
- Programs designed to modify behavior focus on developing healthy eating patterns while addressing any psychological factors related to them. Counseling, goal setting, and self-monitoring techniques may all be used within these programs to aid change.
- Health coaches provide personalized assistance and direction during the weight-loss journey, setting objectives, imparting knowledge, and helping overcome barriers as part of making lasting lifestyle changes.
Weight Loss Statistics By Country
An increasing prevalence of obesity across nations makes losing weight a global priority.
- At over 36% obese and 70% overweight, the US has one of the highest obesity rates globally. Individual states can vary significantly when it comes to rates; some southern states reported up to 35% obesity rates or higher.
- The weight reduction market in the United States is huge and is estimated to be worth billions each year. Mexico boasts one of the highest obesity rates worldwide with about 33% of adults considered obese.
- Repetitive behaviors, poor diets, and access to inexpensive but high-calorie food options all play a role in contributing to this high prevalence.
- Over the past years, obesity rates in Brazil have steadily increased; currently, 22% of individuals are considered obese.
- Changes in eating habits, urbanization, and lifestyle factors have all been blamed for the surge in obesity.
- In the UK, approximately 28% of individuals are considered obese with greater percentages being found among lower socioeconomic categories.
- Childhood obesity has become an increasing challenge with approximately one out of every three children between ages 2-15 being either overweight or obese, and thus constituting an additional health burden.
- Eighty percent of American consumers actively make an effort to consume more fruits and vegetables.
- 19% of Americans shop at farmer's markets for ingredients they need for homemade meals.
- 32% of American adults are overweight while 40% are obese.
- Between 2020-2050, obesity-related expenses are projected to account for anywhere from 5- 14% of healthcare spending.
- Colorado leads all states in America in terms of obesity rate (22.6%) while West Virginia tops it all (38.1%).
- Sugar is considered by 24% of Americans to be the primary contributor to weight gain.
- Recently, China has experienced an alarming rise in obesity; currently, approximately 12 % of Americans are considered obese.
- China is suffering from an obesity pandemic due to a combination of factors, including altered nutrition, urbanization, and sedentary behavior.
- Australia estimates that approximately 30% of individuals are obese, with males being more likely to fall into this category than females.
- Indigenous Australians experience higher rates of obesity compared to the overall population.
- India ranks lower than other nations for obesity prevalence; only four percent of individuals are considered obese in India.
- However, urbanization, shifting dietary trends, and sedentary lifestyles have all contributed to rising rates of obesity across the nation.
- Japan stands out among wealthy nations in having lower obesity rates; only about 5% of individuals currently qualify as obese.
- Lower obesity rates in Japan can be attributed to cultural aspects like portion control, traditional cuisine, and high levels of physical exercise.
Weight Loss Statistics By Demographic
AGE
Different age groups may have different weight loss goals and difficulties.
- Adolescents and young adults are becoming more overweight as time goes on; approximately 20% of teenagers in various nations are classified as either overweight or obese.
- Increased use of technology, sedentary lifestyles, and poor eating practices all play a part in this age group's weight growth.
- Teen weight loss programs often emphasize healthy behaviors and physical activity to achieve weight reduction.
- As people get older, obesity rates among adults increase significantly – from 25-35% in different nations.
- Adults often struggle to prioritize weight-loss efforts due to work, family commitments, and limited free time.
- Adult weight-reduction programs often combine behavioral techniques, exercise routines, and nutritional changes into one comprehensive approach to weight reduction.
- Though older individuals are less likely to be obese than their younger counterparts, maintaining a healthy weight remains essential to good health. Increases in muscle atrophy and potential metabolic changes make weight loss more challenging with age.
- Maintaining a healthy weight is key for older persons looking to manage chronic diseases, increase mobility and decrease their risk of falling. Weight loss therapy for older people typically involves age-appropriate physical activity, strength training, and adopting a nutritious diet plan.
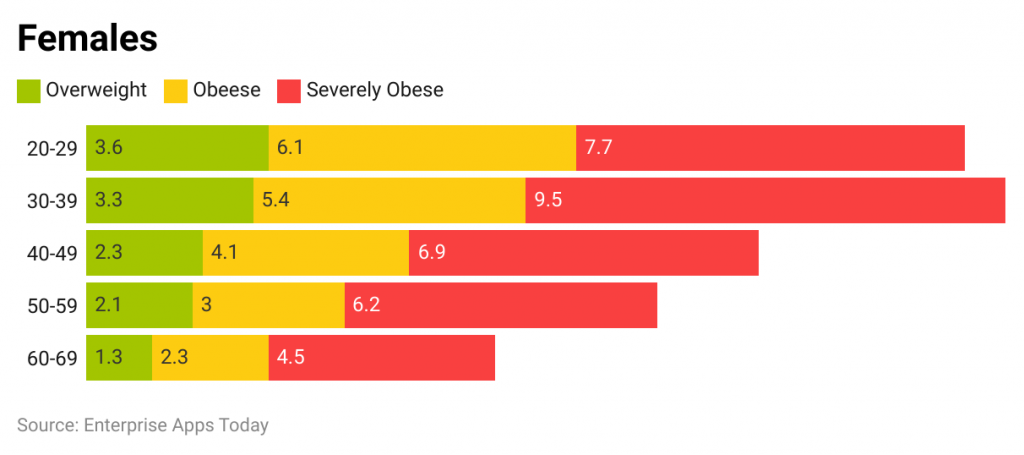
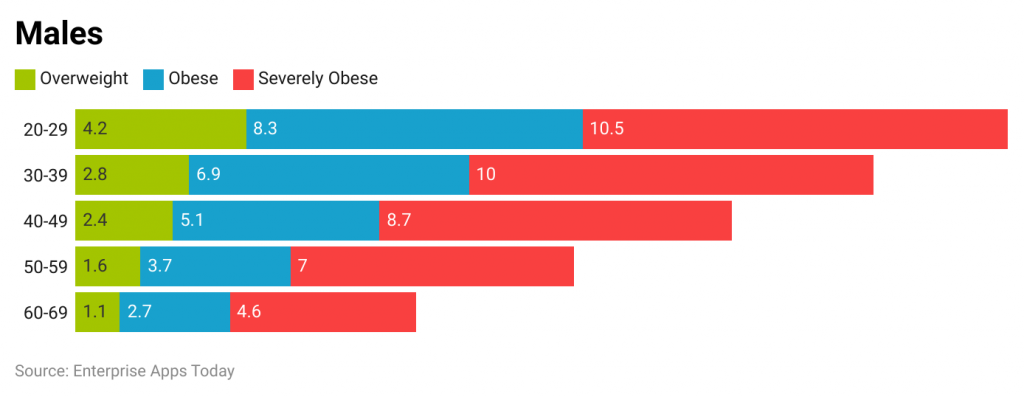
- Of those who were overweight, 49% attempted to lose weight.
- 4% of adults between 40-59 exercised regularly.
- 7% of those between the ages of 20 and 39 who sought to lose weight did so through diet or other means.
- Weight loss can be challenging at any age; according to studies, people often regain weight after experiencing weight reduction.
- Maintaining healthy eating patterns, regular physical activity, support systems, and behavior modification approaches are all effective means for maintaining weight reduction.
(Source: researchgate.net)
GENDER
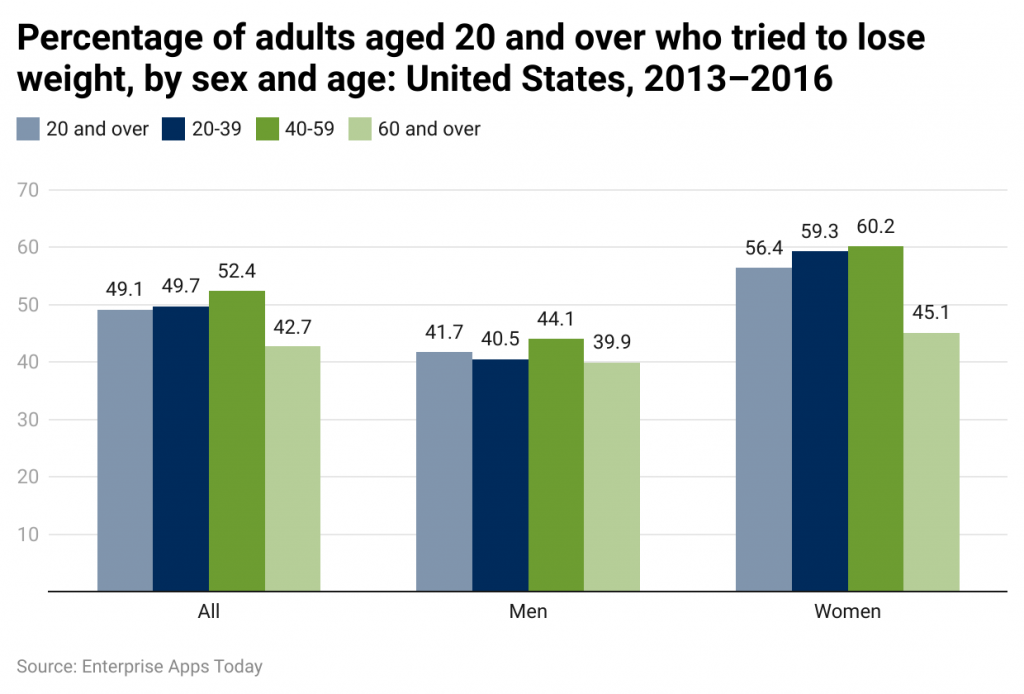
- Men tend to experience slightly higher obesity rates than women across most nations, likely as a result of physiological differences, hormonal impacts, and lifestyle choices.
- But it's important to keep in mind that obesity rates vary between countries and groups; gender disparity might not always exist either. Both men and women work to shed extra weight; their strategies and motivations for doing so may vary accordingly.
- Studies show that women are more likely than men to actively pursue weight reduction strategies such as following a planned diet, enrolling in weight loss programs, or seeking expert assistance for weight management.
- Men may put more focus on physical activity and exercise as a means to lose weight, prioritizing strength training or intensive workouts as weight reduction methods.
- Both men and women often struggle with their bodies, often feeling dissatisfied with them due to social pressures or media influence. Some may seek weight loss goals as a way out.
- Women often face intense social pressure to conform to certain aesthetic standards, which would explain why diets and weight-loss efforts are so prevalent among female populations.
- As more men strive for muscular physiques; body image issues may also arise for them. This could prompt efforts to shed pounds so as to appear more muscular or thin.
- Gender differences can influence weight loss methods. While both men and women generally make diet and fitness changes to achieve weight loss, their specific approaches may vary.
- Women may benefit from portion control, scheduled meals, and calorie counting as part of their weight management strategies. They might also seek assistance from nutritionists or weight loss programs.
- Men frequently turn to physical activity and exercise – such as weightlifting, intense exercises, or sports – as a means to lose weight and build muscles. They could also rely on meals containing proteins for muscle development purposes.
- Maintaining weight reduction may be challenging for both genders. Studies demonstrate that even after initial successes, people frequently experience weight regain.
- To maintain weight reduction over the long haul, one may require long-term commitments to healthy foods, regular physical activity, and behavior modification techniques.
- Men and women alike can successfully maintain weight loss with support networks, accountability frameworks, and ongoing education regarding nutrition and lifestyle choices.
(Source: cdc.gov)
RACE
- Obesity prevalence varies by race and ethnic group in the US. Non-Hispanic Black adults, followed by Hispanic adults and non-Hispanic White adults have among the highest obesity rates according to data provided by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
- Socioeconomic variables, including lower income levels, limited access to healthy food options in certain communities (food deserts), and cultural influences which shape diet preferences and physical activity levels, could all play a part in creating discrepancies.
- Minority groups frequently experience health inequities, including higher rates of obesity and its related conditions such as diabetes and cardiovascular disease.
- Social determinants of health such as uneven access to healthcare, lack of funding for physical exercise programs, or cultural barriers preventing medical care provision all play a part in driving discrepancies in health status between groups.
- Cultural traditions can have an enormous influence on how one perceives their body, including behavior related to weight issues and body image. For example, certain cultural cuisines may feature specific eating habits or consume more calorically dense food which may lead to weight gain.
- Asian non-Hispanic individuals attempted working exercise for 41.4%
- Non-Hispanic Black adults successfully lost weight in 48% of cases
- Adult non-Hispanic whites attempted to lose weight in 49.4% of cases
- People's opinions of weight and physical size vary depending on culturally accepted ideals of attractiveness. Furthermore, socioeconomic disparities have an immense effect on people of various racial and ethnic groups' experiences with weight reduction programs.
- High rates of obesity among underprivileged populations could be the result of a lack of affordable nutrient-rich dietary options and opportunities for physical exercise.
- Socioeconomic considerations may also have an effect on healthcare services like weight management programs, nutrition counseling, and tools to aid weight reduction.
Weight Loss Success Statistics
Success in weight loss may be measured in several ways, including meeting weight reduction objectives, improving health indicators, and maintaining weight over time.
- Studies indicate that people are more likely to achieve success with their weight-reduction efforts by setting specific, attainable objectives.
- Studies indicate that an effective weight reduction goal should aim for 5-10% weight reduction from one's starting weight, as this amount could help improve health results significantly.
- Weight loss has many health advantages for multiple health indicators. Studies have proven the effectiveness of successful weight loss in lowering risks related to obesity such as diabetes and cardiovascular disease as well as improving blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and blood sugar management.
- Dieters often struggle with maintaining weight reduction over an extended period, according to statistics. Many gain weight quickly after experiencing early success with weight loss.
- According to the National Weight Control Registry, which tracks those who successfully maintain weight loss for more than a year, those who have done so typically participate in physical exercise, have a regular eating plan, and benefit from an effective support network.
- Weight loss success may be increased through having a solid support network. According to studies, those who participate in group weight reduction programs and receive help from family or friends tend to experience better results than those trying to lose weight on their own.
- Individual results in terms of weight reduction may depend on factors like genetics, metabolism, and medical issues that exist in each person.
- Individualized approaches tend to be more successful at supporting sustainable weight loss.

(Source: National Weight Control Registry)
Impact on Health
Gaining weight loss can have numerous positive benefits on both physical and psychological health, among others.
- Weight loss has been proven to significantly reduce obesity-related disorders like type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure (hypertension), and cardiovascular diseases. Studies have also demonstrated that even modest weight losses of 5-10% can have dramatic improvements for these health issues.
- Weight reduction can have numerous positive results for those living with type 2 diabetes, including improved glycemic control, decreased insulin resistance, and fewer prescriptions for diabetic medications.
- Studies suggest that those at high risk for type 2 diabetes can significantly lower their risk by making lifestyle adjustments to shed extra weight, such as dieting intentionally or changing eating patterns.
- Losing weight can have profoundly positive effects on cardiovascular health. It can lower the risk of heart disease and stroke, reduce blood pressure and decrease cholesterol (particularly LDL cholesterol levels).
- Studies suggest that weight reduction due to lifestyle modifications could benefit heart health by decreasing oxidative stress levels and inflammation-related indicators.
- An increase in joint tension due to being overweight increases the risk of osteoarthritis and joint discomfort, making weight loss a viable solution for relieving this strain by improving performance and decreasing pain levels in joints.
- Studies show that individuals living with osteoarthritis can see significant improvements in their quality of life, mobility, and joint discomfort by losing as little as 10% of weight.
- Studies have proven that weight reduction can significantly help with sleep apnea, an intermittent breathing condition while you sleep. Studies show that losing weight can decrease both frequency and severity of breathing issues while simultaneously improving the quality of sleep – hallmarks of sleep apnea.
- Losing weight can have a positive impact on mental health outcomes. Studies have linked weight loss with improvements in self-esteem, body image, and general psychological well-being.
- Successful weight losers often report improved quality of life, decreased depressive symptoms, and an increase in confidence after successfully losing weight.
Impact on Economy
Economic conditions can impede access to resources and chances for healthy lifestyle choices, hindering efforts to lose weight.
- Food insecurity, defined as having limited or intermittent access to nutritional foods, can be compounded by economic downturns and poverty.
- Studies indicate a correlation between food insecurity and rising obesity rates, specifically when people rely on low-cost, high-calorie items that contribute to weight gain.
- Low-income people and families may find it challenging to purchase and maintain a diet high in fresh produce, lean meats, whole grains, and other nutritious food options due to financial restrictions; thus increasing their risk of obesity.
- Financial restrictions may restrict access to workout equipment, fitness centers, and gym memberships.
- People may become less willing to invest their resources during times of economic instability, which may impact their capacity for regular physical activity and weight reduction initiatives. Increased stress and anxiety levels can result from economic downturns and financial distress.
- As people turn to food as a form of comfort, stress and emotional issues may lead them to adopt unhealthy eating patterns and overeat, thus hindering attempts at weight reduction.
- Access to healthcare treatments such as weight-reduction programs, nutrition counseling, and other resources may be limited due to economic issues like unemployment or inadequate insurance coverage.
- Due to limited access to healthcare, people may struggle to receive expert guidance in their weight reduction journeys. Furthermore, job insecurity, long hours, and stressful environments may make maintaining a healthy lifestyle harder, thus further complicating efforts toward weight reduction.
- Lack of flexibility and time may hamper efforts at weight loss. Exercise and meal preparation could become impossible due to scheduling conflicts and limited schedule availability; thus sabotaging any weight-loss attempts.

(Source: globalwellnessinstitute.org)
Reason Behind Weight Loss Statistics
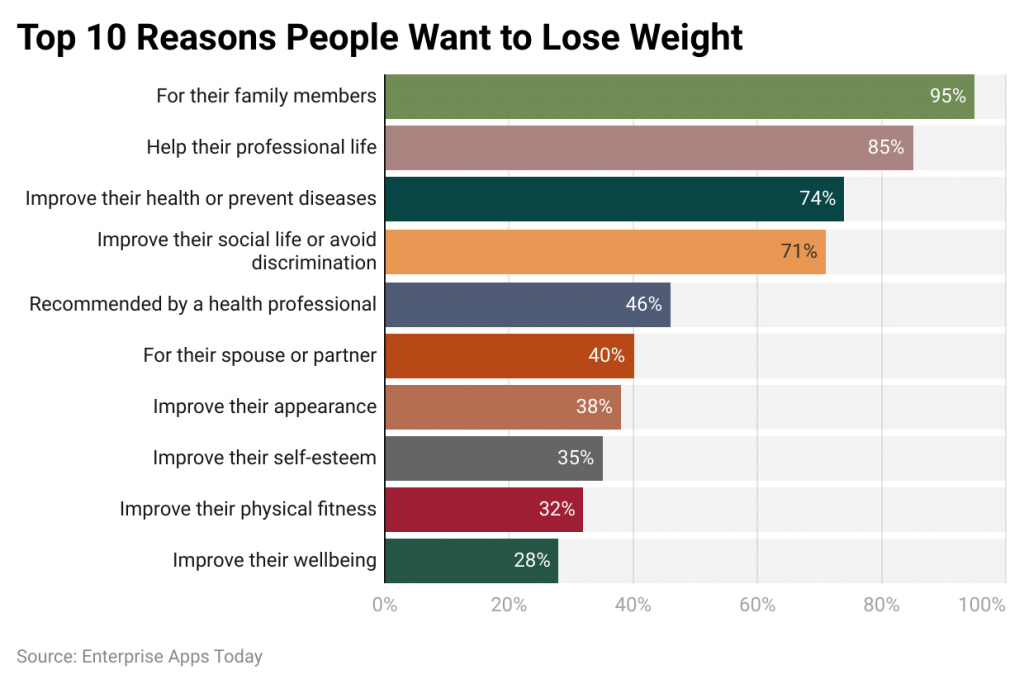
- Many individuals take steps to shed excess weight in order to improve their general health and decrease their chances of chronic diseases like heart disease, diabetes, high blood pressure, and specific forms of cancer. In an attempt to do this, weight loss is often sought as part of this goal.
- Some individuals desire weight loss in order to feel better about themselves and gain more self-confidence; their motivation could come from various social, cultural, or personal influences.
- Sportspeople, athletes, and those involved in physical activity may try to shed excess weight to increase their stamina; agility, or athletic capabilities.
- Doctors may advise patients who are overweight or obese to lose weight in order to treat health concerns or improve overall well-being.
- Lifestyle changes that include eating better and exercising regularly may help lead to weight loss.
- Some individuals seek to lose weight in order to meet cultural beauty standards, wear specific dress sizes, or feel more at ease socially. Personal objectives, such as getting ready for an important occasion or reaching a personal milestone, can serve as further motivations.
(Reference: livestrong.com)
Covid-19 and Weight Loss Statistics
COVID-19 has had an effect on people's health and lifestyle choices, particularly their weight management practices.
- Many individuals have experienced increased worry, anxiety, and emotional hardship as a result of the epidemic. Stress and emotional difficulties may contribute to unhealthy eating behaviors like emotional eating that cause weight gain or make weight loss more challenging.
- Lockdowns, remote work arrangements, and physical activity restrictions all contribute to more sedentary behaviors and reduced opportunities for physical exercise – leading to weight gain or hindering weight loss efforts.
- People's ability to maintain healthy behaviors has been severely undermined by the pandemic's disruption of daily routines.
- Changes in social and physical environments, changes to sleep habits, and meal timing all have an impactful influence on how individuals eat and manage their weight.
- Due to the COVID-19 pandemic, the risk of weight gain increases for youngsters.
- Studies indicate that as a result of this outbreak, certain individuals altered their eating habits as a direct consequence.
- Some individuals reported eating more snacks between meals, changing how often they ate, or increasing their consumption of processed and comfort foods – all of which can contribute to weight gain.
- The pandemic has had serious mental health ramifications, with increased rates of anxiety and sadness being seen among its many effects.
- Changes in weight, including possible weight loss in some individuals, may be affected by factors related to mental health and diet.
Trends and Predictions
Although predicting future patterns in weight loss is challenging due to individual behaviors and social influences, we can identify emerging trends and possibly make some predictions based on what data exists today.
- Future approaches to weight loss will likely emphasize customized plans that focus on individual requirements, preferences, and genetic makeup.
- Wearable technology, genetic testing, and artificial intelligence could play an integral part in designing tailored solutions and tracking their success.
- Health at Every Size movement embraces body acceptance, self-care, and overall well-being instead of solely weight reduction.
- This approach emphasizes physical and mental well-being rather than weight-centric goals, encouraging individuals to adopt healthy behaviors regardless of their weight.
- Psychosocial and mindfulness-based therapies have proven their worth as effective strategies for long-term weight reduction, with programs emphasizing these therapies alongside strategies such as cognitive-behavioral therapy, mindful eating, and stress management.
- Technology and digital weight reduction solutions are projected to become increasingly prevalent, offering those looking for help losing weight access to convenient mobile apps, internet platforms, and virtual coaching programs that provide assistance as well as resources.
- There has been an upsurge in holistic methods that address all facets of health, such as diet, exercise, sleep quality, stress reduction, and mental well-being.
- These comprehensive strategies promote a balanced lifestyle for optimal weight control while acknowledging all its components.
- As more is understood about the significance of prevention, more efforts may be undertaken to shift from simply concentrating on weight reduction towards preventing further weight gain and obesity.
- Prioritizing environments that support healthy lifestyles and lower the risk of weight-related problems is one goal of public health efforts, educational programs, and policy interventions.
- Weight reduction patterns could be affected by changing societal attitudes about body image and weight; with the growing acceptance of different body shapes and a focus on diversity helping reduce expectations of perfection in beauty standards.
Final Thoughts
Weight loss statistics provide vital data on the incidence, patterns, and impacts of weight loss initiatives within communities. They influence research projects, promote evidence-based weight control practices, and help shape public health programs. Policymakers and healthcare professionals can identify high-risk populations, address health inequities, and tailor treatments by analyzing weight loss statistics. Statistics on weight reduction provide valuable insight into the complex relationships among sociodemographic variables, weight, and health. They allow us to understand how socioeconomic position, age gender race, and other factors impact weight reduction results – this knowledge enables the creation of equitable solutions that promote weight management for everyone involved.
Long-term maintenance, behavioral modifications, and health benefits must all be carefully considered when formulating an individualized strategy to tackle weight issues and promote overall well-being. A program featuring techniques, behavioral treatments; healthcare access, and supportive environments must be put in place in order to successfully tackle weight problems and enhance well-being.
Sources
FAQ.
For maximum effectiveness in losing weight, the best and healthiest strategy involves eating less energy while increasing energy output; or put another way: consume fewer calories while expelling more
Calibrate's approach focuses on four pillars of metabolic health - diet, sleep, exercise and emotional well-being - as pillars for weight management success. By prioritizing each pillar separately you may feel better, lose more pounds quickly and enhance overall metabolic wellbeing.
At its core, weight reduction requires you to work within yourself. Once the hard fat that covers organs like liver and kidneys has been shed off, soft fat like that around waist and thighs begins to melt off as soft fat does too; you become leaner and stronger with each loss of organ-covering fat.
As you shed pounds, fat cells begin to contract and produce less leptin, leaving you less satisfied than before. Ghrelin produced in your stomach serves as an indicator to your brain when it is time to eat again; when you lose weight this level increases and prompts an increased desire for food.

By conducting scientific research, I write about illness, health and healthcare. As a professional medical writer, my experience includes creating feature articles for newsletters and websites as well as research news stories for doctors and researchers. Reading has been an integral part of me since childhood - I'm fan of "Friends" and the "Harry Potter series". Before this career, I was employed by a French multinational company. However, my passion for reading led me to pursue writing professionally; my first Amazon-published short story entitled "The envelope that changed our lives" has recently been released. In my free moments, I enjoy long bike rides around town.