Job Growth Statistics By Region, Sector, Trends, Demographic, Pandemic Impact and Economy

Page Contents
Introduction
Job Growth Statistics: Statistics on job growth are essential in understanding the state and trajectory of an economy because they offer insight into the shifting dynamics of labor markets. By measuring net job addition or subtraction over a certain timeframe, employment growth statistics allow policymakers, companies, and individuals to make well-informed decisions regarding workforce planning, investment decisions, or career choices.
Statistics on job growth provide a key measure of economic development as they show whether an economy is expanding, contracting, or remaining stable. Positive employment growth numbers often signal healthy economies with increased consumer spending and company confidence. Conversely, negative or stagnant job growth indicates a slowdown or recession. Furthermore, statistics on employment growth may also be used to highlight developing markets and professions for policymakers as well as job seekers in finding prospective development areas. As such, employment data provides an essential means of measuring an economy's current state and future direction, as well as helping shape policies and initiatives within it.
Editor’s Choice
- From 2020-2030; job growth in the US is anticipated to be 5.3%.
- Nurse practitioners are predicted to experience the highest job growth; between 2021-2031 at 45.7%; 2019 alone saw sectors producing goods create 188,000 new jobs.
- Leisure and hospitality job creation decreased by 47% year-on-year between April 2020 and March 2021.
- President Clinton created 19 million new employment opportunities between June and July of 2022 and 528,000 nonfarm payroll employees were gained; yet by April 2020 20.5 million jobs had been lost from the economy as a whole.
- By 2031, it is projected that employment opportunities across the nation will reach 166.5 million; over that same timeframe childcare service workers have seen their ranks decline by 336,000.
- Since the COVID-19 outbreak, healthcare employment levels have suffered a dramatic decrease. By some accounts, over one and a half million employees may have left healthcare jobs since 2016.
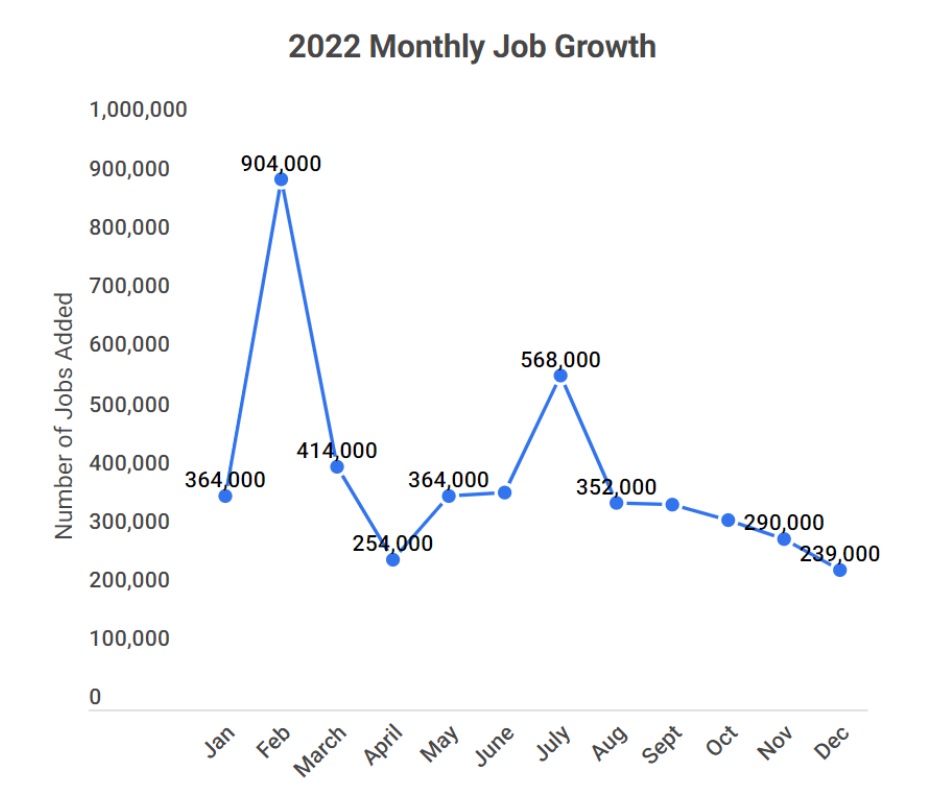
(Source: zippia.com)
What is Job Growth?
Job growth refers to an increase in employment over a set period in an economy or industry, serving as an indicator of its strength and direction as well as health and vitality. Employment data analysis, including newly generated jobs and net changes in employment levels, is frequently employed to calculate job growth figures. When more jobs are created than lost or destroyed, positive job growth occurs. Company confidence, consumer demand growth, and economic expansion all play a part in driving job creation. Factors such as changing consumer tastes, greater investments, favorable government regulations, and technical breakthroughs all can have a positive impact on job growth.
Increased employment has an enormous effect on many important economic aspects. Most notably, it has an immediate influence on the total employment rate – a key indicator of labor market health – with strong job growth lowering unemployment rates and encouraging workforce participation by giving more people jobs. Furthermore, new jobs create economic activity by driving consumer spending and income; when employed people spend money on products or services which increases demand and ultimately propels economic expansion forward. Employment also improves living standards across society as income levels and financial security increase alongside higher living standards as a result.
An analysis of job growth within specific sectors or businesses is an increasingly popular trend, due to technological development, globalization, or shifting customer tastes affecting certain industries differently. Understanding job growth within particular industries can provide information about market trends, investment prospects, and labor needs – key economic indicators which demonstrate its state and direction include job growth. Positive job growth signals an improving standard of living, more available employment options, and economic prosperity; for this reason, politicians, corporations, and people all monitor its rate as an economic indicator and career predictor.
General Job Growth Statistics
Statistics on general job growth provide a detailed look into employment trends across many industries and geographies.
- ILO data indicates that employment has steadily been increasing worldwide over time. By 2022, approximately 58% of working-age populations had secured employment according to employment-to-population ratio calculations.
- Job growth by sector can vary considerably across nations. Service industries – including healthcare, education, banking, and hospitality–often represent significant employment sources in these nations; depending upon their economic structure the significance of manufacturing, construction or agriculture may change accordingly.
- From 1990-2022, there were over 30 million more full-time employees.
- By 2030; an estimated 2.1 million manufacturing positions will be needed.
- Global employment creation relies heavily on small and medium enterprises (SMEs). According to the World Bank, they make up over 98% of businesses globally and account for most jobs across most nations. They provide opportunities for entrepreneurship, creativity, and regional economic development.
- Informal employment continues to play an integral role in global labor markets, characterized by a lack of social security and employment benefits. According to the International Labour Organization, over 60% of employees worldwide take part in this sector – proportions being even greater among workers employed in developing nations.
- Even in an environment of job growth, gender disparities still exist. Women often struggle to find career options and are more likely to work in potentially hazardous and low-paying positions than their male counterparts. Global initiatives are underway to promote gender equality within the workforce and close any existing gaps between genders.
- Education and health services industries saw a 621,000 job growth increase in 2022.
- In 2022; the public sector established 184,000 new positions.
- Leisure and hospitality jobs declined by 47% year-on-year during April 2022.
- Youth unemployment remains an ever-present problem, with young individuals often struggling to gain employment due to limited work experience and access to few job opportunities. According to estimates by the ILO; by 2022 the worldwide youth unemployment rate will surpass that of general unemployment at an estimated 13.2%.
- Automation and technological development may have an effect on job growth. Automation may lead to job losses in some industries; however, new opportunities arise for job categories with digital expertise; data analysis skills, and technological knowledge. As a result, demand has grown for professionals that possess these traits and possess expertise with digital systems or data analysis methods as well as experience using technological devices.
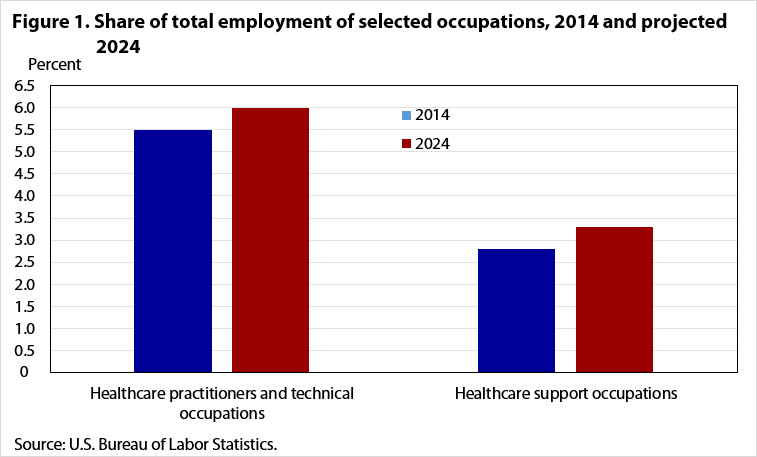
| Occupational Group | 2014 | 2024 |
| Healthcare practitioners and technical occupations | 5.5% | 6% |
| Healthcare support occupations | 2.8% | 3.3% |
(Source: U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics)
Job Growth by Region
Statistics on job growth vary significantly by location due to various factors including financial circumstances, industrial composition, population growth, and government policy.
- The United States and Canada both experienced consistent job growth across North America in 2016. The U.S. economy proved itself resilient with job prospects driven by industries like technology, healthcare, renewable energy, and banking in terms of job creation; natural resources and banking information technology have all seen development due to investments and favorable market circumstances in Canada.
- Europe has experienced mixed employment growth since 2008. While nations such as Germany and the UK have seen improvements; others such as Spain and Greece are still recovering from the financial crisis's aftermath. Overall, industries in manufacturing, services, and digital technology have helped generate jobs.
- Texas has long experienced rapid job growth. This success is the result of its diverse economy, business-friendly climate, and sizable population; Texas outpaced the national average job growth from 2010-2022 at around 19.3%.
- California has experienced steady job creation despite its size and economic struggles, with 13.2% job creation growth between 2010-2022 – slightly less than the national average growth rate. Some Californian regions, like Silicon Valley, have seen notable job gains.
- Massachusetts has developed an impressive knowledge-based economy supported by industries like technology, healthcare, and education. Employing an emphasis on specialized sectors, Massachusetts experienced job growth of roughly 10.7% between 2010-2022 – which remains impressive given the national average growth.
- China remains an impressive source of job creation in Asia despite a shift towards more service-based economies, thanks to a robust industrial and technological sector that has expanded and provided more jobs. India too has experienced growth thanks to robust business process outsourcing and IT sectors, despite ongoing unemployment issues and skill gaps.
- Florida has experienced rapid population growth, which has provided significant opportunities for job development. Between 2010-2022, employment grew 19.3% – equaling the national average rate.
- North Dakota's oil and gas sector was instrumental in driving job creation. Between 2010-2022, job growth saw an incredible 44.7% surge. However, it's important to bear in mind the unpredictable nature of natural resource-related businesses which could impact long-term sustainability.
- Latin America experiences variable job growth. Some nations such as Mexico and Brazil have seen moderate job creation thanks to industries like auto manufacturing, aerospace engineering, and IT; whereas in others like Venezuela and Argentina political turmoil has reduced employment creation rates significantly.
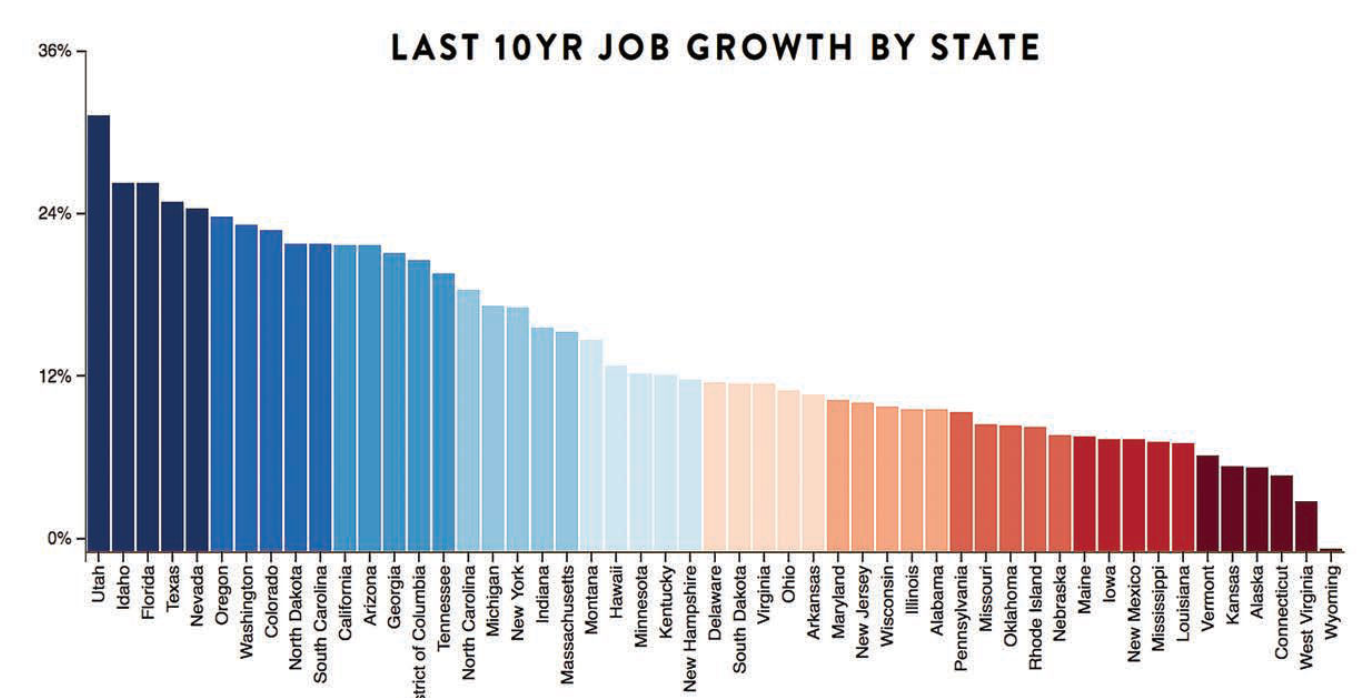
(Source: slenterprise.com)
Job Growth by Industry and Sector
Statistics on job growth by industry and sector provide important insight into the shifting dynamics of the labor market as well as highlight potential development opportunities.
- Recent years have witnessed tremendous job creation within the technology industry. Thanks to digital transformation and innovation initiatives, this sector experienced 31% job growth between 2010-2022 – far surpassing other industries.
- An aging population and increased demand for healthcare services have been the driving forces behind job creation in the healthcare industry. Between 2010-2022, job growth in this industry averaged 22.7 percent – making it one of the fastest-growing sectors.
- With 179,000 new jobs added since February 2022, leisure and hospitality topped all other industries for employment growth. Professional & Business Services saw impressive gains with 596k new positions added during that month alone despite influenza's widespread spread.
- Information and utility industries were the only two industries with no new jobs created in February 2022.
- Numerous sectors, including consultancy, legal services, accountancy, and scientific research are covered under this umbrella term. With the increased demand for specialist services driving its expansion – professional and commercial services experienced an average 15.7% employment increase between 2010-2022 – professional and commercial services provided a remarkable surge.
- Banking, insurance, investments, and asset management all fall under the realm of financial services. Economic development, globalization, and an increase in financial transactions are major driving forces behind job growth in this industry. Financial analysts, bankers, investment advisers, and actuaries have all seen increases due to changing global economic requirements.
- Construction plays an integral part in infrastructure and economic development. Following its steep decline during 2008's global recession, this sector has gradually seen renewed activity as evidenced by job growth of 16.6% between 2010-2022; reflecting increasing construction activity.
- Renewable energy industries have emerged as one of the major sources of employment growth as sustainability and clean energy continue to gain prominence. From 2010-2022 alone, the job growth rate averaged 24.5% due to rising investments in renewable energy projects.
- Manufacturing has undergone significant change, from automation and offshore outsourcing to job growth of approximately 5.6% between 2010-2022; slower than other industries but nonetheless contributing new jobs.
- Particularly in areas with well-known tourist sites; hospitality and tourism have played an instrumental role in job creation. From hotel management, food and beverage services, event organizing, and tour guiding to hotel operations – this industry has provided jobs in hotel management, food and beverage services, event organizing, and tour guiding by hotels; restaurants, travel agencies, and tour operators. However, the COVID-19 pandemic may have had an adverse impact on employment growth within this sector.
- E-commerce's growth has had a substantial effect on the retail industry. While conventional brick-and-mortar retail has experienced difficulties, online retail has grown considerably. Retail and e-commerce jobs increased by 9.2% between 2010-2022.
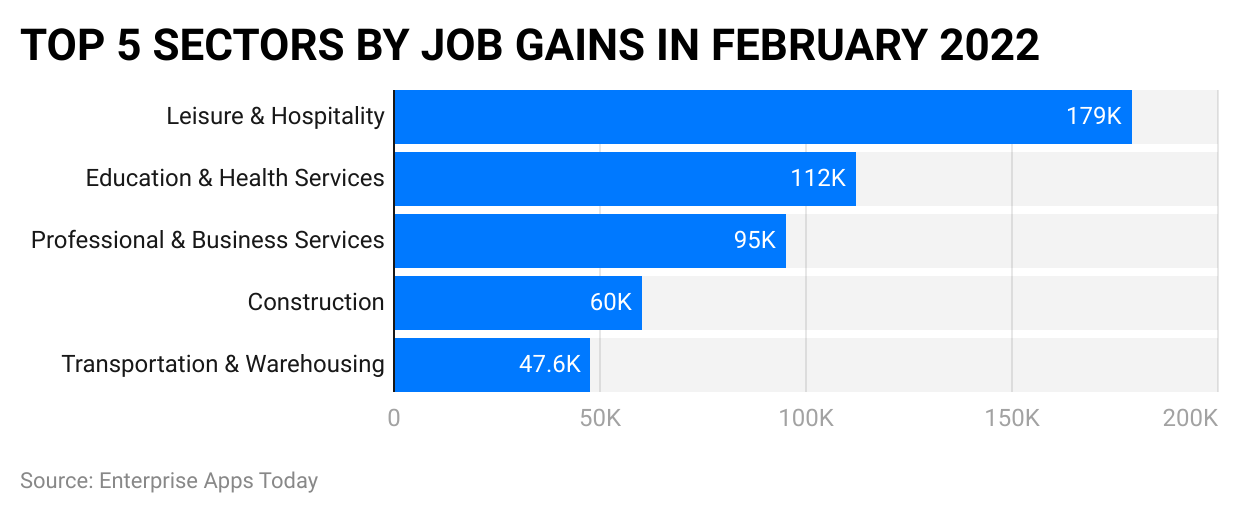 (Reference: zippia.com)
(Reference: zippia.com)
Job Growth by Demographic
Statistics on job growth by demographic categories provide insight into employment possibilities and labor market dynamics among various population groupings, yet information may be lacking about job creation by these demographic groupings.
- Gender disparity was once common in the labor market, with men and women experiencing different rates of employment growth. Recently, however, there has been a movement towards gender equality. For instance, between 2010-2022 in the US women's employment increased by 15.7% while men's increased by 14.8%; though these numbers can differ depending on industries or professions.
- Age-related job growth rates depend on experience levels, educational attainment, and retirement patterns. When entering the workforce for the first time, younger individuals tend to see faster rates of job growth compared to their elderly colleagues who may work less due to retirement considerations; yet many older employees choose to work longer hours more frequently which bolsters overall employment growth in this age group. It can be challenging to provide specific numbers due to the limited information readily available about job growth rates across age groups.
- There remain significant racial and ethnic disparities in the labor market, and rates of employment growth vary depending on your group. African Americans and Hispanics traditionally experienced greater unemployment rates and slower job growth rates when compared with White people and Asian people; attempts have been launched to promote diversity and inclusion and help close these gaps; for up-to-date data regarding employment growth rates by race/ethnicity, it is essential that you consult current labor market studies or official sources.
- An education degree is vitally important in terms of both work options and job growth. People with bachelor's degrees or more experienced job growth at 18.9% between 2010-2022 compared with 9.8% among those holding only high school diplomas or lower. Of course, these rates of growth may still differ according to particular sectors or occupations
- People with impairments often face particular difficulty when searching for and maintaining employment. Aims have been set forth to promote inclusive hiring practices and assist people with disabilities in jobs; although exact figures on job growth rates by disability status remain unavailable. More comprehensive data may be found by consulting papers and researching disability employment issues.
- Different geographical areas – urban, suburban, and rural areas – might experience different rates of job creation. Due to the concentration of businesses, services, and infrastructure in urban centers, job growth tends to be stronger there while rural regions may face difficulty creating employment opportunities resulting in emigration or diminished work prospects.
- Immigrant employment data reflect their employment experiences. Immigration can play an integral part in supporting economic development for some businesses and sectors where there is a labor shortage; however, language issues, acceptance of credentials and cultural differences may pose particular difficulties to immigrants.
- Employment growth opportunities depend heavily on a person's socioeconomic level. Individuals from lower-income backgrounds may face additional barriers to finding quality work that limits job development; programs emphasizing social mobility, job training, and skill development aim to support economic success among those from lower socioeconomic origins.
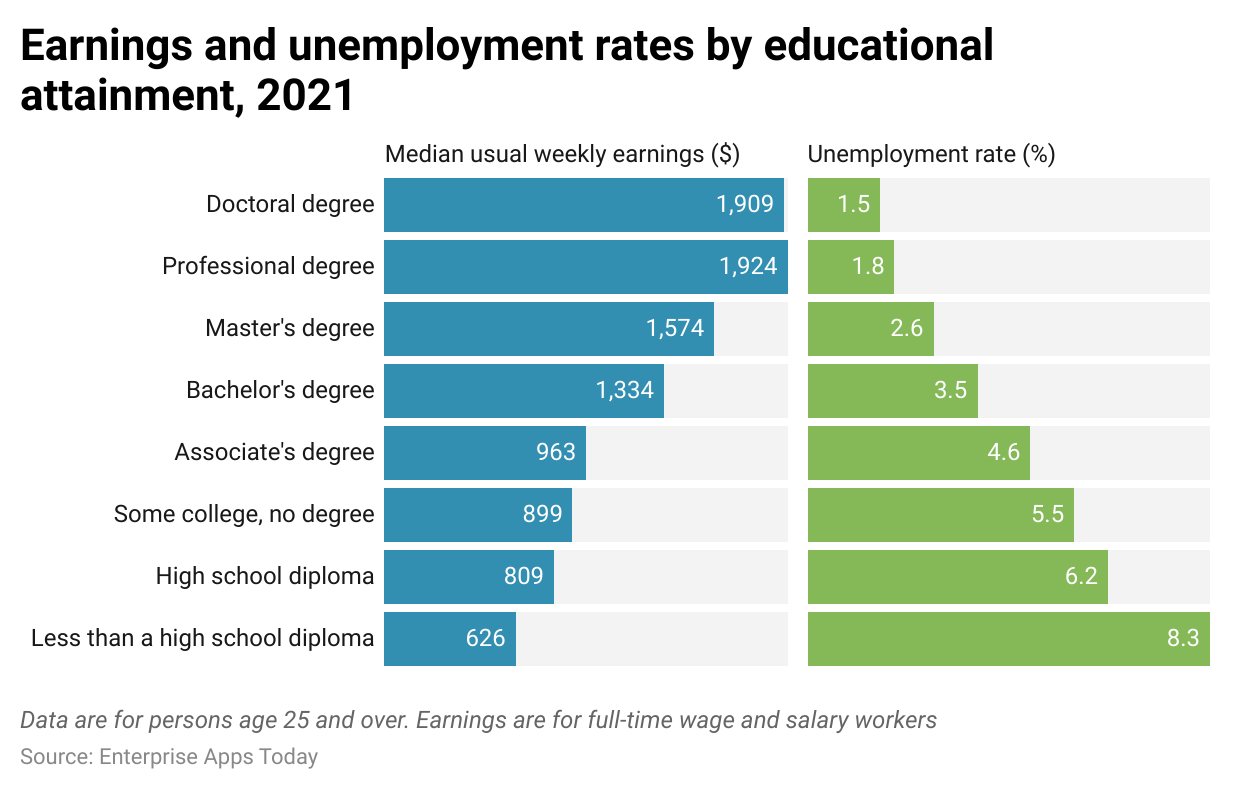
(Reference: bls.gov)
Job Growth by Pandemic
The global health crisis has had an extraordinary effect on employment levels during the COVID-19 pandemic.
- As the epidemic swept through, lockdown measures were implemented, leading to numerous businesses closing both temporarily and permanently – leading to a drastic decrease in employment across many industries. Travel, hospitality, retail, and entertainment were particularly hard hit.
- As a result of the pandemic, industries across sectors experienced uneven job growth. Technology, e-commerce, logistics, and healthcare saw notable job gains, while industries that rely on having physical locations such as restaurants, bars, and personal services- saw significant employment losses.
- This epidemic accelerated the use of flexible work schedules. When compared with employment requiring a physical presence, jobs that could be completed remotely such as office-based tasks and professional services experienced less interruption and thus altered both natures of work and labor market dynamics.
- In an effort to aid companies and prevent job loss, several governments enacted stimulus packages and employment retention programs designed to help financially-impacted people while encouraging industries that were particularly hard hit to retain jobs.
- As of February 2022; COVID-19's effects had affected 13.5 million jobs; across America; and led to a 9 million employment shortage deficit.
- Job growth gradually resumed as immunization efforts expanded and some restrictions were eased; employment levels began increasing across industries including manufacturing, construction, and professional services.
- Tourism and entertainment, which rely heavily on interpersonal interactions, experienced slower job growth than other sectors that transitioned from analog to digital operations.
- The epidemic has altered the job economy and accelerated certain trends. Digital literacy, e-commerce, data analysis, and remote collaboration skills are increasingly sought-after; some individuals upskilled or reskilled themselves to remain employable despite changing labor market circumstances.
- The epidemic had a devastating impact on the gig and informal workers who lacked social safeguards or employment security, particularly those working within unorganized sectors with little social safety net or job protections. Many experienced income losses or job dislocation, underscoring how vulnerable this workforce can be when crises strike.
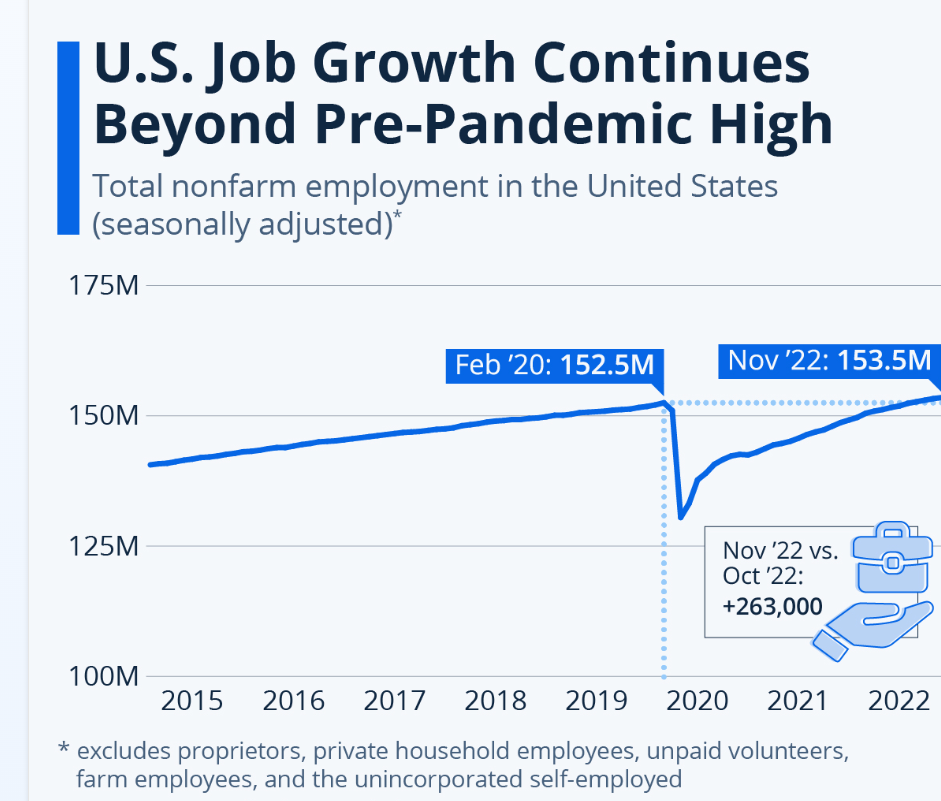 (Source: statista.com)
(Source: statista.com)
Impact of Job Growth on the Economy and Environment
Job growth has an immense effect on both the economy and the environment.Economic Effect:
- Job creation is integral to economic growth; studies indicate a linkage between them that shows GDP increasing for every 1% increase in employment. Furthermore, creating jobs drives consumer spending, company investment, and tax collections which all support overall economic expansion.
- Job-generated income benefits both individuals and households alike, providing additional disposable money and elevating standards of living. In turn, increased job revenue stimulates consumer spending across various industries thereby spurring economic activity across a spectrum of fields.
- Productivity gains and technological breakthroughs often coincide with job creation. Businesses invest in R&D research in order to increase productivity while creating employment, thus stimulating innovation; economic competitiveness, and long-term growth.
- Small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) and startups play an essential role in job creation. Small businesses play an essential role in stimulating innovation; creating jobs and cultivating an atmosphere conducive to economic diversification and resilience.
Effect on the Environment
- An increase in employment could have an impact on greenhouse gas emissions. Some industries, including industry and transportation, contribute significantly to carbon emissions; however, hiring more employees in sustainable, energy-efficient, renewable industries could contribute to lower emissions levels and help shift our economy toward sustainability.
- An increase in employment may require greater use of resources, including electricity, water, and raw materials. Initiatives geared towards sustainable employment growth emphasize resource-efficient behaviors such as the circular economy and green technology to limit environmental consequences associated with industrial techniques.
- Many professions play an essential role in protecting and conserving the environment. Careers such as conservation, waste management, environmental consultancy, and renewable energy directly support sustainability initiatives and biodiversity preservation efforts.
- Green economic transition offers great job prospects. According to projections by the International Labour Organization (ILO), employment in energy efficiency and renewable energy sectors alone will rise by millions over several years.
- Regulations designed to safeguard ecosystems and reduce pollution have the potential to create jobs in an indirect fashion. Businesses and regulatory bodies often respond by hiring for environmental management and compliance positions.
Job Growth Trends and Predictions
Predictions and trends regarding job growth depend upon many variables, including economic considerations, technical developments, demographic shifts, and government regulations. Although some aspects of future job development remain unknown.
- As digital innovation accelerates, it is expected that job growth will accelerate with it. Experts expect there to be considerable demand for positions related to data analysis, artificial intelligence, cybersecurity, software development, and digital marketing as well as robot maintenance/programming jobs that become increasingly common as automation and robots are widely adopted into society.
- Green industries are expected to experience job growth as the economy transitions towards being more environmentally sustainable and eco-friendly. Governments and corporations placing greater priority on environmental preservation will likely see jobs created within renewable energy, energy efficiency, waste management, and sustainable agriculture sectors.
- As the population ages and healthcare demand grows, healthcare industry employment should increase dramatically. Employment could expand across fields like healthcare practitioners, administrative personnel, and technology development for healthcare services.
- The COVID-19 epidemic has spurred increased use of flexible scheduling and remote work arrangements. These trends are expected to persist even after their effects have subsided, creating new job opportunities in virtual communications, remote collaboration technologies, and associated services.
- Demand for new skills will drive job growth. Digital literacy, data analysis, programming, problem-solving, and flexibility will become essential across various sectors; lifelong learning programs will play a pivotal role in equipping individuals with new employment prospects.
- Due to technology's integration into healthcare, particularly telemedicine and digital health solutions, job growth is expected as more experts specialize in areas like telemedicine, health informatics, and medical device development.
- Demographic trends such as population aging and the rise of millennials will impact job growth, with financial services, entertainment, and other industries that cater to senior citizens increasing. Furthermore, the desire for work-life balance and social impact among millennials may play a part in expanding nonprofit and socially responsible company sectors.
- Retraining and job changes will become necessary as technology progresses and industries adapt, both of which will have a direct effect on employability. With an ability to adapt quickly to shifting job needs and develop new skills, job development should become simpler.
Bottom line
The statistics regarding job growth are essential in illuminating the current trends and patterns of employment across various industries and demographic groups. They reveal that the labor market is a dynamic entity and that multiple factors impact the number of jobs created. Economic conditions, technical advancements, governmental policies; and demographic shifts all contribute to employment creation but it is important to note that the growth of jobs varies between sectors and geographical regions.
While industries such as healthcare; technology; renewable energy, and services are expected to experience a significant increase in job creation; others may find themselves facing challenges or changes due to automation and changing consumer preferences.To create a more equitable labor market, measures should be taken to help people with disabilities, reduce young unemployment rates, end gender and racial inequities, and foster inclusive job development.
Education and skill enhancement investments can also help individuals to adapt to changing employment requirements and seize new opportunities. Employment trends can be affected by unexpected, unpredictable circumstances such as economic downturns or technological advances; therefore job growth estimates alone do not provide sufficient insight. To successfully navigate a changing employment market and take advantage of opportunities that arise with developing sectors and technologies, individuals and organizations will need to adapt, reskill and embrace lifelong learning in order to remain employable and take advantage of all available opportunities.
FAQ.
A fulfilment associate saw the highest month-over-month job posting growth at 230% according to LinkedIn's list of fastest-growing occupations, followed by Big Data developers (+80%), cashiers (79%), dishwashers (+79%) and shop associates (+1 48% and restaurant servers (+1 113) plus those that specialize in them like translation specialists or retail associates who have all experienced tremendous expansion since starting.
On average, employment growth rates typically fall within the range of 5%-8% per annum; some occupations develop faster than this by between 9-13% or even 14-15%. When growth drops between 2-4 per cent it is considered slower than usual and movement in either direction by one per cent indicates no change while any decrease of over 2 indicates a decline.
Automation has had an enormous effect on job growth rates. The word processor and typewriter jobs have experienced an alarming decline of 38.2% since 2008. Due to automation, two-thirds of individuals currently employed within this industry may lose their employment within 10 years due to automation. Other quickly diminishing occupations include parking enforcement officers (-35%) and respiratory therapy technicians (56%).
Yes, an increase of 8 per cent in job growth is positive because it exceeds average rates. Although 70% growth may seem unrealistic at first glance, an 8% rate could easily create hundreds or even thousands of new employees depending on available positions

Barry is a lover of everything technology. Figuring out how the software works and creating content to shed more light on the value it offers users is his favorite pastime. When not evaluating apps or programs, he's busy trying out new healthy recipes, doing yoga, meditating, or taking nature walks with his little one.