College Dropout Statistics
Page Contents
12 million, or 60.9% of graduate and undergraduate students, are enrolled in college. Each year, 20.7%, or 4.1 million, graduate with a degree.
Yet, dropping out is more than common all across the world. People quit their degrees midway for several reasons and never return to academics.
Some try to find other ways to continue. For example, a student can buy an essay paper online with expert guidance by Studybay. Buying an essay, papers, and research essays improve grades, says Kaylan Dennis, a famous writer.
However, that does not reduce the dropout rate. How many people drop out of college and how many people graduate college? Why do students drop out of college?
In this blog, we will explore dropout statistics in detail. You will walk away with comprehensive information to support your research or studies.
General College Dropout Statistics
- 17% of learners in the US quit their semester last year due to several reasons. Interestingly, both men (18%) and women (16%) show the same mentality.
- 32% of undergraduates quit their degrees without completion. 24.1% of new students in bachelor programs leave their institution within 12 months.
- Around 40% of all undergrads drop out. It resulted in 39 million dropouts in 2020. However, 944,200 went back to their classes that semester.
- The US ranks 19th out of 28 countries in average graduation rate for colleges. The ranking is from the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD).
- Only 14.7% of those with bachelor’s degrees complete their programs. The average graduation rate college for associate’s degree enrollers is 37.5%.
- Most people who quit a four-year program are between 24 and 29 years. 52% of them have left their studies without a certificate.
30% of dropouts re-enroll in the hope of completing their education.
You May Also Like To Read:
College Dropout Demographics
It is necessary to understand the demographics of students who leave education. You will spot interesting trends and patterns that give you meaningful insights.
Here are a few facts worth considering:
- Learners aged between 20 and 23 have a college dropout rate of 51%. The rate for undergraduates between 24 and 29 years is 52%.
- Most folks who quit midway are between 35 and 64. It shows even older learners are prone to quitting studies.
- Asian students are less likely to drop out. They have a dropout rate of 19.1%, the lowest among all ethnicities.
- The white population is 7.9% less likely to quit their degrees. In comparison, the black population is 33.8% more likely to leave their education.
- Women are 20% less likely to walk away from higher education. They also surpass men in the number of new enrollments.
- The pandemic saw a 70% decline in enrollment for males in 2020. It reflects one of the leading causes of leaving academics during this period.
- Students with disabilities have 58.7% of dropping out. A lack of infrastructure and costs account for the reasons to leave.
The Most Common Reasons for Dropping Out
Students leave their degrees for a number of reasons. It has to do more than expensive programs or failing in the finals.
Below are a few insights that will help you develop a better understanding:
- 31% of people put an end to their studies to look for a job. The high demand in the job market in countries like the US fuel the dropouts.
- Another 31% of students quit their degrees because they are unsure what to study. They don’t want to spend on a degree that adds no value to their life.
- The high cost of living forces 29% of learners to not return to classes. Moreover, they are not in a position to afford tuition.
- Around 28% of people enrolled in different programs cannot continue due to mental and physical health issues. The pandemic also made the situation worse for most of the population.
- Approximately 25% of students leave their degrees to support their families financially. They cannot afford to put time and money into continuing their education.
- 24% of enrollers don’t find higher education useful or applicable. They prefer to pursue other aspirations or goals in life.
- 28% of people quit their studies to become entrepreneurs. They idolize personalities like Bill Gates and Zuckerberg, hoping to follow in their footsteps.
- Academic pressure makes 28% of learners leave. Additionally, 54% decide to quit as they find it difficult to balance work and study.
The World Economic Forum found additional reasons for dropouts:
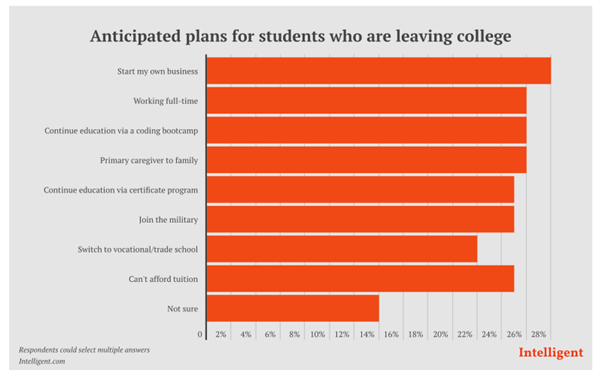
(Source: weforum.org)
Impact on Career and Economy
College dropouts tend to earn less and find fewer opportunities for employment. However, some join certificate courses to work as developers, data analysts, and designers.
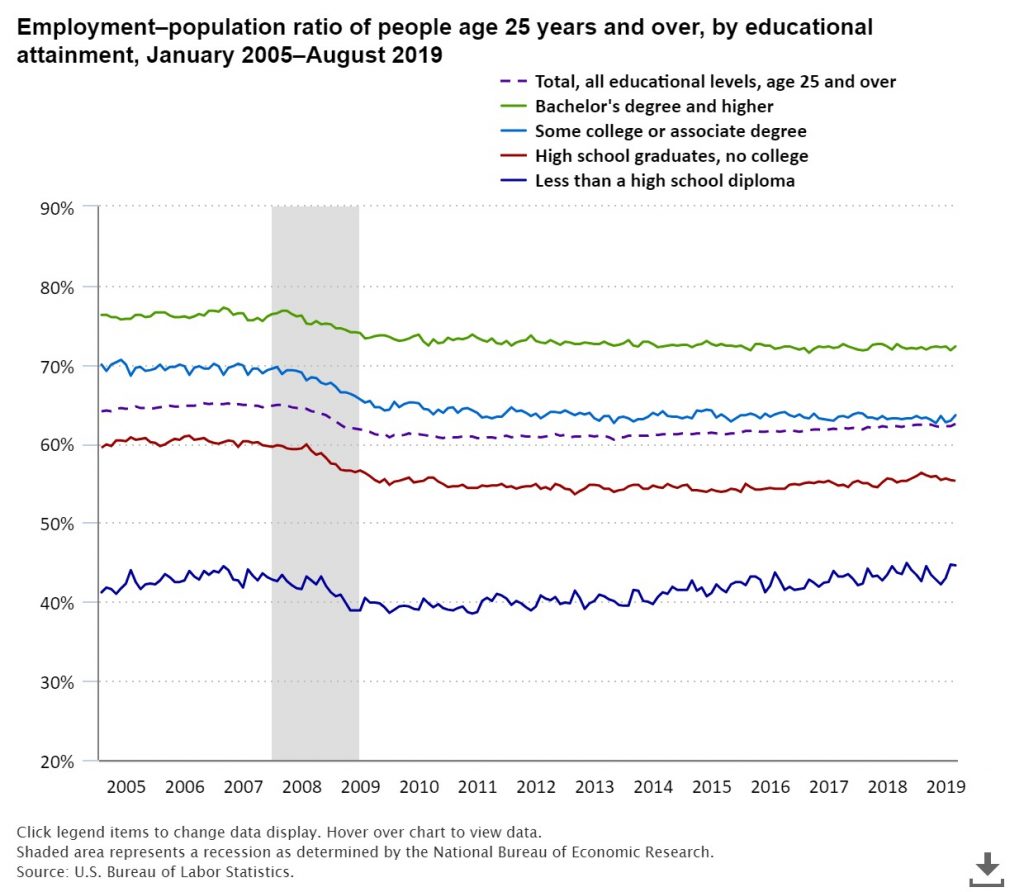
(Source: bls.gov)
Below are a few insights to understand how leaving studies affects work life:
- 60% of high school graduates without a bachelor's degree are employed. In comparison, 72.3% of bachelor's degree holders work in a profession.
- People who went to college but did not complete their program have an unemployment rate of 5.5%. It is 17% higher compared to the national average.
- Adults aged 25 and over without a degree, but some college earn $899 on average weekly. It is 14.9% lower than what the average worker earns.
- The student loan debt has reached a staggering $1.5 trillion. Over 2 million borrowers could not repay their debts in time.
- The cost of dropping out is around $3.8 billion every year. Taxpayers are predicted to account for $32 billion in losses in the next 10 years due to loan defaults.
- A graduate earns 35% more compared to a bachelor's dropout. It may result in low-income families that experience more dropouts.
- 53% of learners from low-income families delay or quit their studies due to financial struggles. In comparison, only 11% of higher-income learners choose not to enroll in further studies.
College Enrollment Statistics
A percentage of students decide to rejoin classes after they decide to quit. Moreover, new learners enroll in different programs to build a positive outlook.
Let's take a look at some interesting facts to discover more about the situation:
- The total undergraduate enrollment is predicted to increase by 8% between 2020 – 2030. However, it declined by 9% between 2009 and 2020, according to the NCES.
- 70% of female high school graduates enrolled for further studies immediately in 2021. In comparison, 55% of males did the same.
- Only 9% of dropouts re-enrolled in their courses in the 2021 – 2022 academic session. However, only 71% of those in four-year institutions continue, compared to 57% in community colleges.
- 47% of unenrolled adults think about going to college. Additionally, 61% thought about continuing their classes in recent years.
- 55% of dropouts are hesitant to enroll due to the cost of the program. 45% stay away from education due to inflation, while 38% are still weighing costs.
- Aspirants are showing more interest in programs other than a bachelor's degree. There is an increase of 4.8% in enrollments in other courses in community colleges.
The government and educators are working hard to reverse the trend of dropping out of college. The dropout rate has also started declining after a spike during the pandemic.
Sources

Barry is a lover of everything technology. Figuring out how the software works and creating content to shed more light on the value it offers users is his favorite pastime. When not evaluating apps or programs, he's busy trying out new healthy recipes, doing yoga, meditating, or taking nature walks with his little one.